Resistance Calculator
Understanding Series and Parallel Resistor Combinations
When it comes to designing electrical circuits, knowing how to combine resistors effectively is crucial. Whether you’re a student, an electronics hobbyist, or a professional engineer, understanding the principles behind series and parallel resistor networks can help you build and troubleshoot circuits with ease. This article explores the fundamentals of resistor combinations, explains the differences between series and parallel arrangements, and demonstrates how to calculate equivalent resistance using our powerful Equivalent Series and Parallel Resistor Value Calculator.
The Basics of Resistor Combinations
Resistors are passive components used in circuits to control the flow of current and to divide voltages. They come in various values, and by combining them in series or parallel, you can create a desired total resistance even if the exact resistor value is not available off the shelf. This flexibility is particularly useful in electronics design, allowing for precise tuning of circuit parameters.
In a series combination, resistors are connected end-to-end, forming a single path for current flow. The total resistance is simply the sum of all individual resistances. Conversely, in a parallel combination, resistors are connected across the same two points, providing multiple paths for the current. Calculating the equivalent resistance for resistors in parallel is slightly more complex but offers the advantage of reducing overall resistance.
Series Resistor Combinations
Series resistor combinations are straightforward. When resistors are connected in series, the total or equivalent resistance Req is given by:
This means that if you have three resistors with values of 10 ohms, 20 ohms, and 30 ohms, the equivalent resistance is 60 ohms. The principle behind this is based on the fact that the same current flows through each resistor. Therefore, the voltage drop across each resistor adds up to the total voltage drop.
Series connections are especially useful when you need to achieve a higher resistance than what is available in a single component. They are often used in applications where voltage division is required, such as in sensor circuits, LED drivers, and timing circuits.
Parallel Resistor Combinations
Parallel resistor networks are designed to reduce the overall resistance of the circuit while providing alternative pathways for current flow. The formula to calculate the equivalent resistance for resistors in parallel is:

For two resistors (R1 and R2), the formula simplifies to:

For example, if you have two resistors of 10 ohms and 20 ohms in parallel, the equivalent resistance would be approximately 6.67 ohms. This calculation demonstrates how the overall resistance decreases as more resistors are added in parallel.
Using a parallel resistor calculator or a parallel circuit calculator simplifies these calculations significantly. With the help of these tools, you can instantly compute the equivalent resistance without manually working through the formulas. This is particularly useful for circuits that incorporate multiple resistors where manual calculation might be error-prone.
The Role of Our Equivalent Series and Parallel Resistor Value Calculator
Our calculator is designed with versatility in mind. It allows you to input up to 10 resistors, whether arranged in series or in parallel, and provides the equivalent resistance in ohms, Kohms, and Mohms. By integrating this tool into your workflow, you can ensure quick and accurate results while learning more about circuit design along the way.
The user-friendly interface ensures that even beginners can understand how to compute parallel resistance quickly. The calculator functions as a parallel resistance calculator by automatically applying the correct formulas based on your input. This is especially helpful when working with resistors in parallel, which can sometimes be challenging to calculate manually.
Why Combine Resistors in Parallel?
Combining resistors in parallel offers several benefits:
Lower Equivalent Resistance: When you need a resistance value lower than what’s available in a single component, parallel configurations come in handy.
Increased Current Capacity: In a parallel setup, the current divides among the branches, reducing the burden on any single resistor.
Reliability: If one resistor fails, the overall circuit may still function because the remaining resistors continue to provide a path for the current.
These advantages make parallel resistor configurations a popular choice in many practical applications, including power distribution circuits and electronic filters.
Practical Applications in Electronics
The principles behind series and parallel resistor combinations are applied in various fields:
Consumer Electronics: Devices like smartphones and laptops often use resistor networks to manage voltage and current effectively.
Automotive Industry: Modern vehicles use sophisticated resistor networks for functions such as sensor circuits and control systems.
Industrial Controls: In industrial settings, precise resistance values are crucial for sensors and control circuits, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
A deep understanding of these concepts is essential for troubleshooting and optimizing these systems. This knowledge not only helps in the design phase but also in maintenance and repair, where diagnosing circuit issues quickly is paramount.
Integrating the Calculator Into Your Workflow
Our Equivalent Series and Parallel Resistor Value Calculator is designed to be a seamless part of your project toolkit. Whether you’re drafting a new circuit or debugging an existing one, this tool is your go-to resource. Here’s how you can make the most of it:
Quick Calculations: Instead of performing lengthy calculations manually, simply enter your resistor values into the calculator.
Multiple Units: The calculator displays results in ohms, Kohms, and Mohms, making it easier to interpret the data based on your circuit’s requirements.
Error Reduction: Automated calculations reduce the chance of mistakes, which is especially important in complex circuits with many resistors.
Learning Tool: As you experiment with different resistor configurations, you’ll gain a better understanding of how series and parallel combinations affect overall resistance.
Bridging Theory and Practice
The beauty of electronics lies in the combination of theoretical knowledge and practical application. While textbooks provide the necessary equations and concepts, tools like our calculator bring these theories to life by offering real-time, hands-on learning. Whether you’re a student trying to grasp the fundamentals or a seasoned engineer looking to verify your calculations, mastering the art of resistor combinations is a valuable skill.
Enhancing Your Circuit Designs
Understanding and correctly applying series and parallel resistor combinations can greatly improve your circuit designs. Accurate calculations lead to better-performing circuits, whether it’s a simple LED circuit or a complex microprocessor system. By integrating both traditional calculation methods and modern digital tools, you can optimize your designs for efficiency and reliability.
Moreover, the use of keywords such as parallel resistor calculator, resistors in parallel, parallel resistance calculator, parallel circuit calculator, and parallel resistance in your research and design documentation will make it easier for others to find and understand your work online. This integration of SEO-friendly practices ensures that your technical documentation not only serves its purpose but also reaches a wider audience.
Final Thoughts
In summary, combining resistors in series and parallel is a fundamental skill in electronics. The ability to calculate equivalent resistance accurately is essential for designing robust circuits. With the advent of digital tools like our Equivalent Series and Parallel Resistor Value Calculator, performing these calculations has never been easier. Whether you’re building your first circuit or refining an existing design, the integration of both theory and practical tools will enhance your projects and deepen your understanding of circuit behavior.

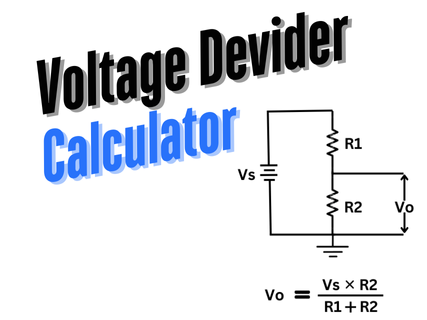
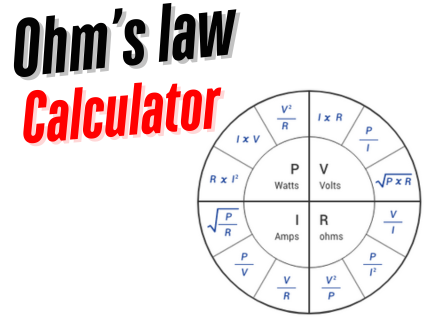
[…] Calculate Now Calculate Now Calculate Now […]